Abstract
The European Union (EU) is advancing sustainability initiatives through the Digital Product Passport (DPP) and the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR). These initiatives promote product transparency and environmentally conscious design across product lifecycles. Icecat, a leading provider of open and structured product data, is uniquely positioned to support these efforts today. Particularly through its capacity to provide detailed model-level information that meets the requirements of the DPP and ESPR. This paper explores the role of model, batch, and item-level data in enabling product traceability and sustainability, and how Icecat can facilitate compliance with these new EU regulations.
Introduction
The EU’s transition to a sustainable, circular economy is underpinned by regulations that promote resource efficiency, product durability, and waste reduction. The Digital Product Passport (DPP) is a key tool for achieving these goals, offering a digital record of essential product information throughout its lifecycle. Furthermore, The Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR) complements the DPP by setting mandatory standards for product design that emphasize longevity, repairability, and recyclability.
This positions Icecat as a crucial player in this regulatory landscape, focusing on its ability to provide model-level product data and the value of open access to this information. Icecat’s platform can significantly ease the burden of regulatory compliance while promoting transparency and sustainability in product supply chains.
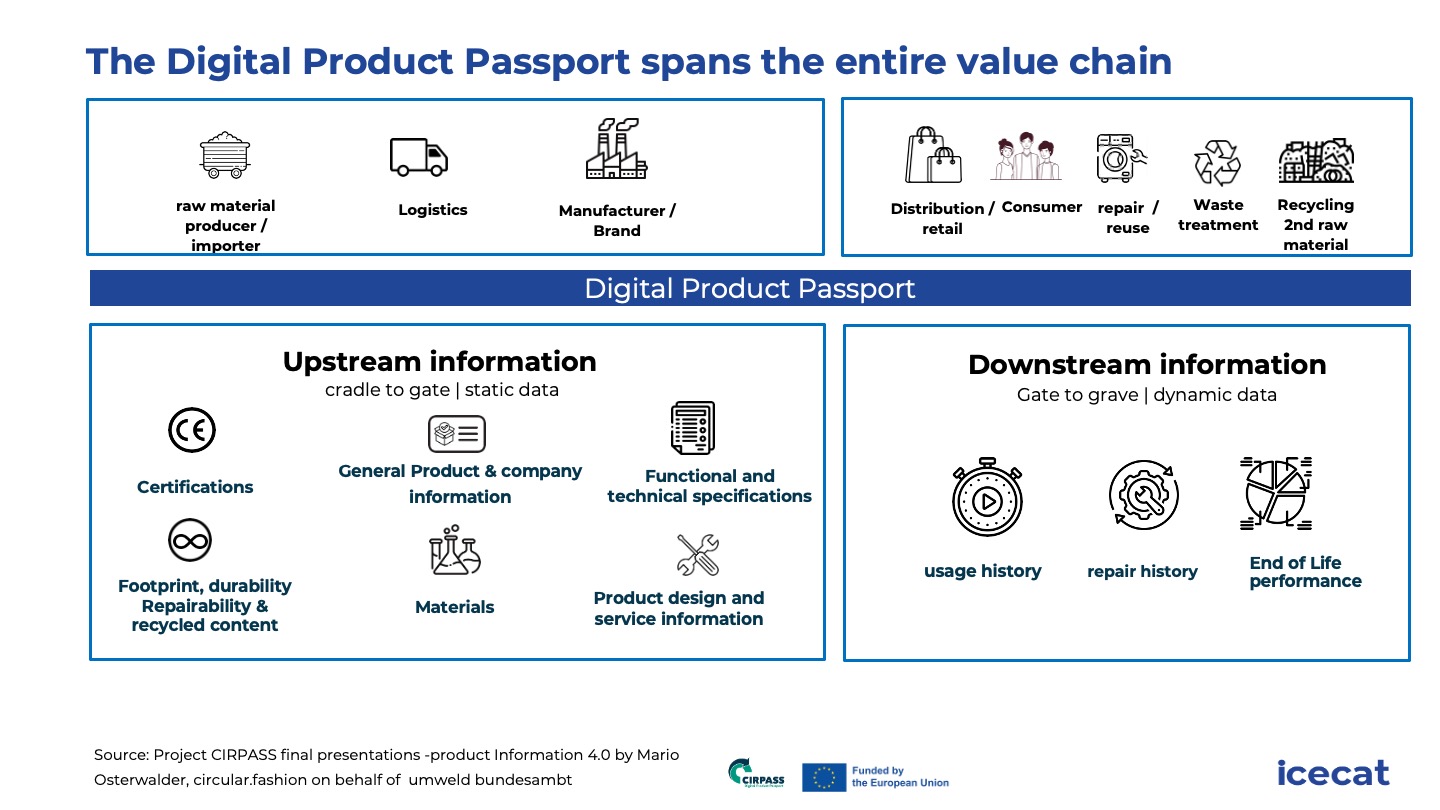
Levels of information in the Digital Product Passport
The DPP is expected to require product data at varying levels of detail depending on the specific use case. These levels—model, batch, and item—are critical to ensuring transparency throughout the product lifecycle. The appropriate level of detail supports different stakeholders, from consumers and regulators to manufacturers and recyclers, in making informed decisions about product use, repair, and disposal.
1. Model-Level Information
Model-level data refers to information that applies to an entire product line, regardless of specific batches or units. This level of detail typically includes general product specifications, materials used, energy efficiency ratings, and regulatory compliance certifications (e.g., EPREL, WEEE).
Use Cases:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that a product model complies with sustainability regulations.
- Marketing: Highlighting sustainability attributes, such as the percentage of recycled materials used or compliance with eco-label standards.
- Consumer Information: Providing customers with data on energy consumption, environmental impact, and eco-certifications.
2. Batch-Level Information
Batch-level data covers specific production runs or groups of products manufactured under the same conditions. This information is useful for tracking the origin of materials, verifying batch-specific certifications, and managing quality control.
Use Cases:
- Traceability: Identifying the source of materials and ensuring they meet sustainability and ethical sourcing standards.
- Quality Control: Isolating products for recall or investigation based on batch-specific defects.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Demonstrating the use of certified or recycled materials in a particular production batch.
3. Item-Level Information
Item-level data refers to information specific to an individual product unit. This level of granularity is essential for tracking ownership, repair histories, warranties, and the product’s end-of-life management.
Use Cases:
- Repair and Maintenance: Accessing repair instructions or part replacement information tailored to a specific item.
- End-of-Life Management: Providing individualized recycling or disposal guidelines based on the materials and components used in a specific product unit.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: Tracking a product’s lifecycle, including remanufacturing or refurbishment efforts, to ensure it is part of a reuse or recycling program.
Icecat’s Role in Supporting the DPP and ESPR, Today
Icecat is exceptionally well-positioned to support both the DPP and ESPR today, particularly in providing open, model-level product data that aligns with the EU’s sustainability goals. Here’s how:
1. Model-Level Data Accessibility
Icecat aggregates comprehensive product information from a vast range of manufacturers, covering industries such as electronics, appliances, and office supplies. The data includes model-specific details, such as:
- Technical specifications and product features
- Energy efficiency ratings and certifications
- Materials used and eco-label compliance
This model-level data forms the foundation for DPP-related requirements. Icecat’s open platform makes much of this information freely accessible to the public, ensuring that stakeholders have access to the sustainability data they need. For example, consumers can easily check whether a product meets EU energy efficiency standards or contains recycled materials.
2. Open Platform for Public Access
One of Icecat’s key strengths is its open platform, which allows unrestricted access to a wealth of product data. This is critical for meeting the transparency goals of the DPP. By providing open data, Icecat ensures that both consumers and businesses can access important information about product sustainability, such as carbon footprints, materials, and recyclability.
This openness not only benefits the general public but also aligns with the DPP’s vision of making product lifecycle data accessible to all stakeholders, thus promoting informed decision-making and sustainable consumption.
3. Standardized Data Formats
Icecat collects product information from manufacturers in standardized formats such as XML, JSON, and CSV, which makes it easy to integrate with other platforms and systems. This is particularly important for ensuring compliance with DPP and ESPR requirements, as it enables seamless data exchange across the EU’s digital infrastructure.
The use of standardized data formats ensures that businesses can quickly adopt the DPP framework and provide the necessary sustainability data for their products without needing to create custom data solutions.
4. Support for Sustainability and Compliance
Icecat already provides extensive data on product sustainability at the model level. This includes energy ratings, material composition, and environmental certifications—all essential for meeting the requirements of the ESPR and the DPP. By making this data accessible, Icecat helps businesses comply with EU regulations and enables consumers to make more environmentally conscious purchasing decisions.
For example, a product’s energy efficiency rating or recyclability information can be easily accessed through Icecat’s platform, supporting both compliance and transparency objectives.
Conclusion
As the EU moves forward with initiatives like the Digital Product Passport (DPP) and the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR), the demand for transparent, accessible, and detailed product information will increase. Additionally, Icecat is uniquely positioned to meet this demand by providing open, model-level product data that aligns with the goals of these sustainability regulations.
Through its comprehensive product repository, standardized data formats, and open platform, Icecat supports both regulatory compliance and sustainability efforts. By facilitating easy access to critical product information, Icecat helps ensure that consumers, businesses, and regulators have the tools they need to foster a more sustainable economy.
Irina is a Digital Marketing Lead with a passion for creating impactful marketing strategies that drive brand success. When she’s not crafting campaigns, she enjoys writing, traveling to new destinations, discovering exciting new things, and seeking outdoor adventures.